16
Mar
What are the Types of Ketamine?

Knowing about the different types of ketamine helps to understand its applications in ketamine-assisted mental health treatment. In this blog post, we will discuss the differences between the forms of ketamine available for use in medical treatment of pain and mental health disorders in Ontario.
Ketamine has long been used as an anesthetic but more recently has shown potential for treating mental illness as well. Different forms of chemical molecules have different effects on the human body. Before we dive deep into the types of ketamine available for use, a brief chemistry lesson.
The Chemistry of Ketamine
Ketamine was first synthesized in 1962. Ketamine is a chiral compound, meaning its molecular structure is not symmetrical. There are two versions of the ketamine molecule that naturally occur, called enantiomers. The Latin words for right and left are rectus (R) and sinister (S). Chemistry describes molecular orientation using these concepts. In medicinal therapies, these molecules’ spatial arrangements have different consequences.
What is an enantiomer?
A pair of molecules that are mirror-images of each other. They have the same connectivity, but the opposite three-dimensional shapes, so they cannot be superimposed on each other.
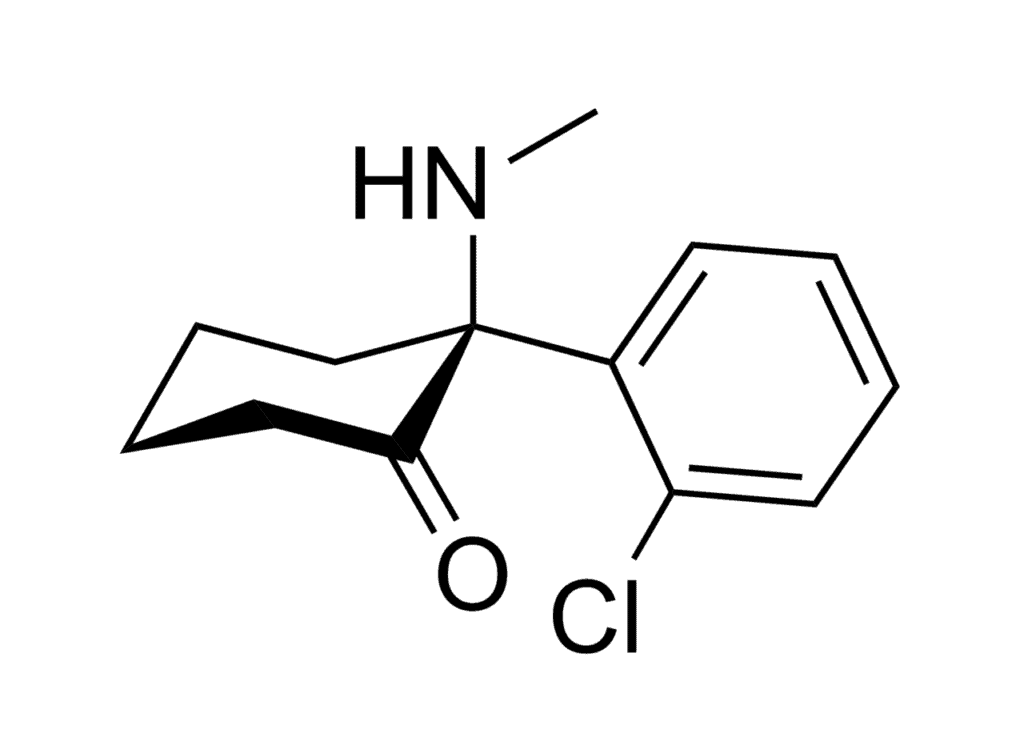
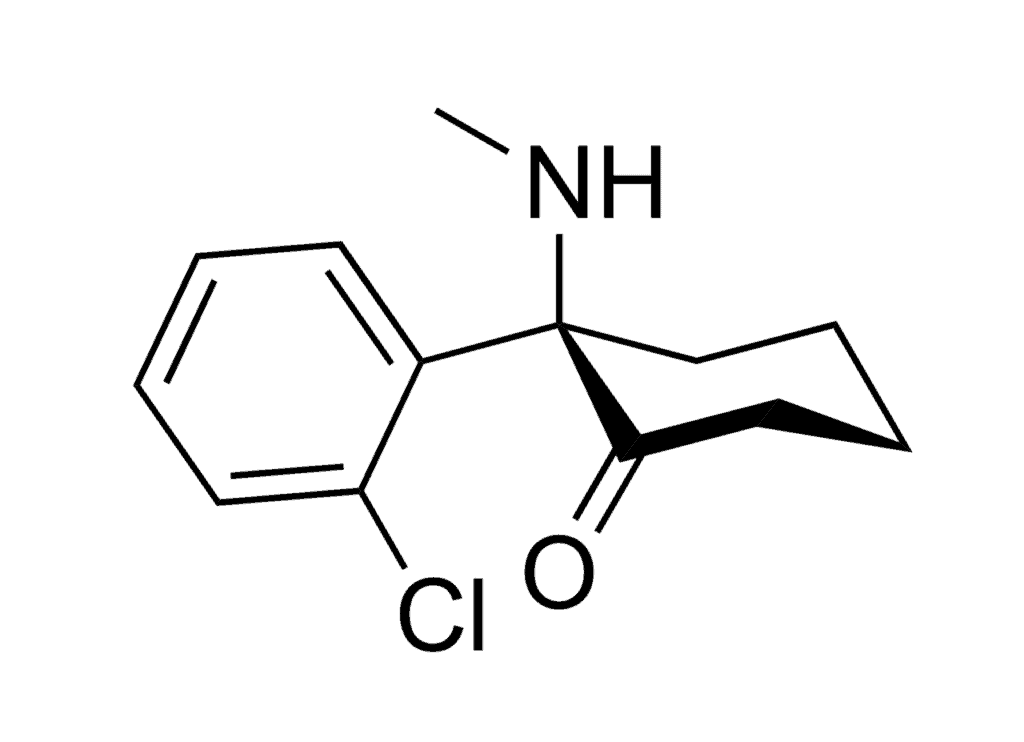
The more commonly occurring enantiomer of ketamine is S-ketamine, also called esketamine. The less common active enantiomer is R-ketamine, which has never been marketed as an enantiopure drug (only one form of enantiomer) for clinical use. R-ketamine is commonly called arketamine. The R and S forms of ketamine have different effects on the body.
R,S-Ketamine
This common formulation of ketamine is made up of both mirror-image enantiomers, R and S. This is the generic form of ketamine and has the longest history of use in medical practice. It was approved for use in the US in 1970 and was generally used as an anesthetic and for pain relief. R,S ketamine remains one of the safest anesthetics available on the market, as it does not lower heart rate and blood pressure like other medications.
R,S-ketamine is available in many delivery forms including, nasal, oral, sublingual and intravenous injections.
S Ketamine or Esketamine
S-ketamine, also known as esketamine, has stronger anesthetic quailities. Esketamine has been extensively studied and has been found to produce fast antidepressant effects. Esketamine is only recently approved in Canada (2021) under the name Spravato. It is available by prescription only and must be taken in a supervised medical setting. Esketamine is the most commonly used form prescribed when undergoing ketamine-assisted psychotherapy.
Due to its increased affinity for NMDA receptors (receptors in the brain), esketamine demonstrates stronger effects compared to R-ketamine. This makes it beneficial in clinical settings, especially when quick action is required.
R Ketamine or Arketamine
R ketamine, or arketamine, is left form of the ketamine enantiomer. It has less anesthetic power than S ketamine, because it is less effective in binding NMDA receptors in the brain. Arketamine is not approved for medical use in Canada.
However, recent research suggests that R ketamine may have a stronger and longer-lasting antidepressant impact than S ketamine. This feature is being widely studied for treating depression and other mental health conditions.
It’s unusual interaction with NMDA brain receptors makes arketamine interesting. R-ketamine shows much weaker activity than S-ketamine, but researchers think the R-form may regulate brain receptors instead of blocking them (as S-ketamine does). This may cause fewer side effects, less hallucinogenic and dissociative effects, and a longer-lasting antidepressant effect.
What is the Difference Between R and S Ketamine?
The biggest differences between R and S ketamine are found in their chemical structure and how they work in the body. Both enantiomers interact with brain NMDA receptors differently with regard to effect or agonist activity.
S ketamine is more potent, stronger as an anesthetic, and acts faster as an antidepressant. Side effects are more likely with this potency. R ketamine, a weaker anesthetic, produces longer-lasting antidepressant effects and less adverse effects. This has raised interest in arketamine for long-term mental health treatment.
Only R,S-Ketamine and S-ketamine are approved for use in Canada.
Exploring Ketamine for Major Depressive Disorders
To make the most of these enantiomers in clinical settings, it’s important to know their specific features and how they’re used. As research proceeds, under Health Canada’s careful supervision, these versions of ketamine will show their full therapeutic potential which will enable more advanced mental health treatments for depression and other disorders.
At Caledon Clinic our highly experienced team will support you in selecting a treatment plan that is most suitable for your medical needs. Contact us today to learn more about ketamine therapy and how we can assist you.
References:
Ketamine – Wikipedia
Spravato – Health Canada


